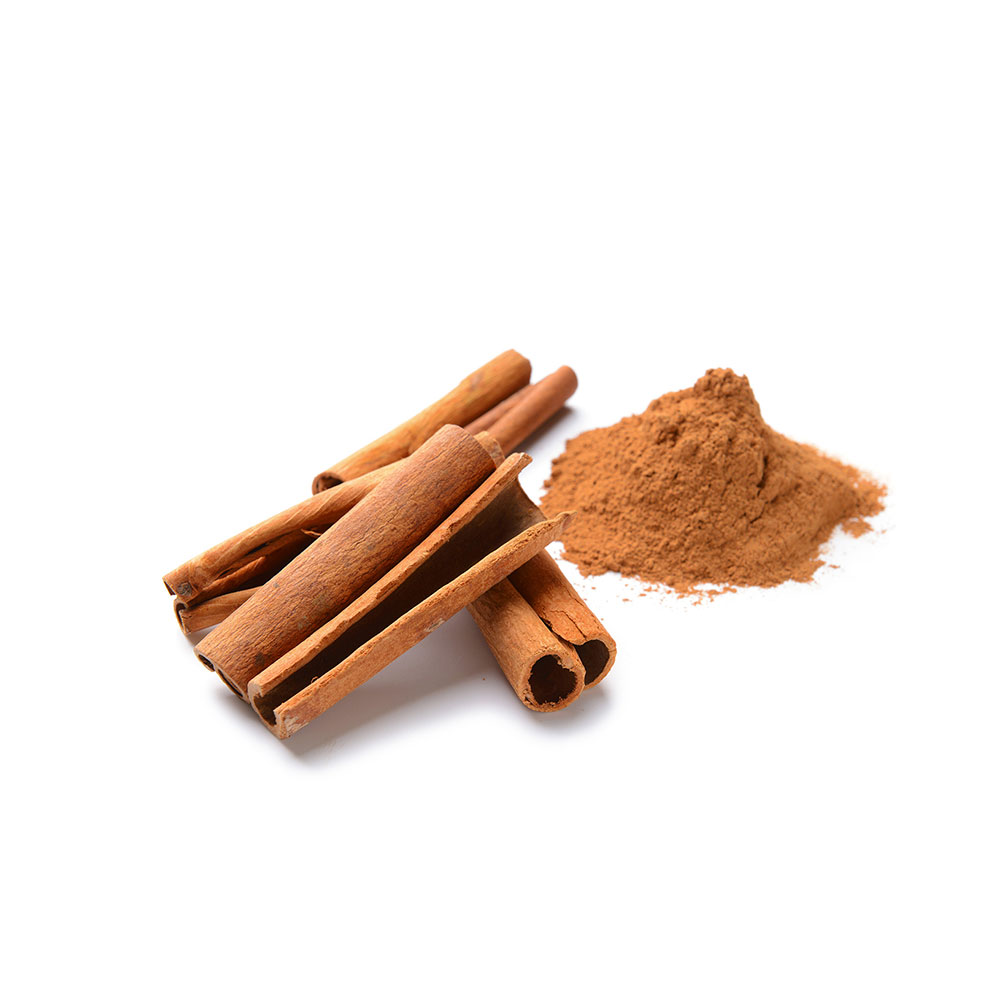
Cinnamon Magic Properties: Boosting Longevity
Cinnamon Magic Properties:
Exploring Cinnamon Magic Properties like Health Benefits, History, and Effects on Blood Sugar Management and Antioxidant Activity
Many people have loved the unique flavor and smell of cinnamon for many years. People use it in cooking and it offers health benefits. People know cinnamon for its ability to help manage blood sugar and its strong antioxidants. A versatile natural remedy and a tasty addition to many dishes around the world.
History of Cinnamon Use or How Humans Discovered Cinnamon Magic Properties
Cinnamon’s journey through history is as rich as its aroma. Cinnamon comes from tree bark in countries like Sri Lanka, India, Indonesia, and China.
Ancient civilizations prized cinnamon for its exotic fragrance and medicinal properties. Ancient Egyptians used it for embalming.
In ancient Rome, it was a symbol of wealth and luxury. Many nations often burn it at funerals. Cinnamon also held a prominent place in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda for its therapeutic benefits.
During the Middle Ages, cinnamon became a highly sought-after commodity in Europe, traded along the legendary Silk Road. It had a value comparable to gold and people used it as currency, medicine, and flavoring. Today, lots of cooks use cinnamon in cooking to make sweet and savory dishes taste better.

Health Benefits of Cinnamon
- Antioxidant Properties
One of the most studied aspects of cinnamon is its antioxidant content. Antioxidants are compounds that combat oxidative stress in the body, which can lead to chronic diseases and aging. Cinnamon contains polyphenols, such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, which act as antioxidants. These compounds can prevent free radicals from damaging cells and causing diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
Studies have shown that cinnamon extracts can increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the body. Cinnamon can reduce the risk of chronic conditions by enhancing the body’s natural defenses against oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is connected to inflammation and damage.
Cinnamon is renowned for its potential to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that regulates glucose (sugar) metabolism in the body. Individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes often have difficulty using insulin effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Research indicates that cinnamon compounds, particularly cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic acid, can mimic insulin function and increase insulin sensitivity in cells. This allows cells to better utilize glucose from the bloodstream, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Regular consumption of cinnamon has been shown to reduce fasting blood sugar levels and improve HbA1c (a marker of long-term blood sugar control) in people with type 2 diabetes.
Also, cinnamon can help slow down the digestion of carbs, which lowers the increase in blood sugar levels after eating. This effect can be beneficial for anyone looking to manage their blood sugar levels, not just those with diabetes.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a normal immune response, but long-term inflammation is connected to diseases like heart disease, arthritis, and some cancers. Cinnamon has compounds that can reduce inflammation and lower health risks.
Cinnamaldehyde, the main active compound in cinnamon, has been shown to inhibit the release of inflammatory mediators and suppress the activation of inflammatory pathways in the body. By reducing inflammation, cinnamon may contribute to improved overall health and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Cognitive Function and Neuroprotection
Emerging research suggests that cinnamon may support brain health and cognitive function. Cinnamon extract may help protect brain cells and reduce inflammation in animal studies.
These findings suggest a potential role for cinnamon in neuroprotection and possibly in mitigating the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. However, more research is needed to fully understand cinnamon’s effects on brain health in humans.
- Antimicrobial Properties
Cinnamon has been traditionally used as a natural preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. Cinnamon essential oil is made from the bark or leaves of the cinnamon tree.
It has strong antimicrobial properties that help fight off many types of bacteria and fungi.
This antimicrobial effect is attributed to compounds like cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and cinnamic acid, which can inhibit the growth of pathogens and foodborne bacteria.
Incorporating cinnamon magic properties into food preparation may help extend shelf life and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Using Cinnamon as a Supplement and Food
Cinnamon can be enjoyed in various forms, each offering its unique benefits:
- Ground Cinnamon: The most common form, ground cinnamon is versatile and can be sprinkled on oatmeal, yogurt, or used in baking and cooking.
- Cinnamon Sticks: These are ideal for infusing flavor into hot beverages like tea or mulled wine and can be used in stews or rice dishes for a subtle cinnamon aroma.
- Cinnamon Essential Oil: Extracted from cinnamon bark or leaves, cinnamon essential oil is highly concentrated and should be used sparingly. It can be diluted and used topically or in aromatherapy for its therapeutic effects of cinnamon magic properties.
When using cinnamon as a supplement, it’s essential to choose high-quality sources to ensure potency and purity. Cinnamon supplements are available in capsule or extract form and are often standardized to contain specific amounts of active compounds like cinnamaldehyde.
Cinnamon in Culinary Delights
Cinnamon’s warm, spicy flavor makes it a beloved ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes:
- Desserts: Cinnamon pairs beautifully with apples, pears, and chocolate in pies, crisps, cakes, and cookies.
- Beverages: It adds depth to hot drinks like coffee, hot chocolate, and chai tea, as well as refreshing cold beverages like iced tea or smoothies.
- Savory Dishes: Cinnamon can be used in marinades for meats, added to curries and stews, or sprinkled on roasted vegetables for a hint of sweetness and warmth.
Incorporating cinnamon into your daily diet can not only enhance flavor but also provide a range of health benefits, from supporting blood sugar management to promoting antioxidant activity and beyond.
Conclusion
Cinnamon magic properties lie not only in its enticing aroma and versatile culinary uses but also in its potent health-promoting properties. From ancient times to the modern age, cinnamon has been revered for its ability to aid in blood sugar management, exert antioxidant effects, and potentially protect against chronic diseases.
Whether enjoyed as a spice in your favorite dishes or as a supplement for its therapeutic benefits, cinnamon continues to captivate hearts and minds worldwide with its rich history and enchanting flavors. Embrace the magic of cinnamon and explore its multifaceted benefits for your health and well-being.
Incorporate cinnamon into your daily routine and savor the warmth, flavor, and health benefits it brings—a true testament to the timeless allure of this extraordinary spice.
Written By Doctor Olga Almathhan